Total Project Management: Endless Visuals, Infinite Inspiration.
Explore
Effective project management is about tapping into what inspires and drives you. Is it tackling tough challenges, making a real difference, sparking innovation, honing your skills, or growing personally? Explore the topics below to start your journey.
Understand.
Examine the content to understand its significance, analyze the context of the illustration, and assess its relevance to your role. Consider how it can help you tackle a problem, improve a process, increase your knowledge, enhance your abilities, or apply an innovative solution.
Learn.
Once you find a topic that drives and excites you, explore it further. Read related articles on this blog, review the templates provided, and understand how to apply theory to practice. There are numerous articles that offer insights, step-by-step directions, and helpful tips to simplify complex topics. Start with the introductory pieces and gradually dive into the more advanced material.
Share your experience with ganntpost by commenting on the articles.
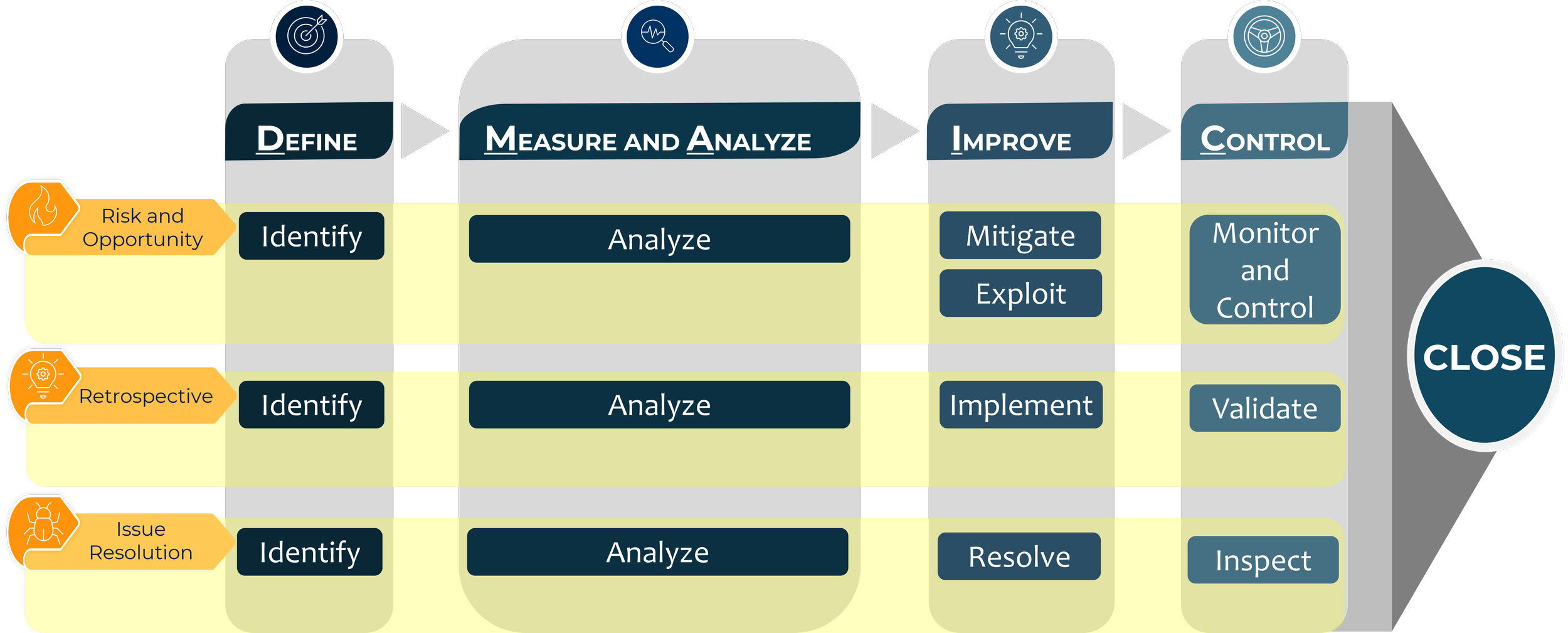
DMAIC offers a systematic framework to identify inefficiencies and opportunities, analyze their impact, implement necessary changes, and sustain improvements. Organizations can utilize the DMAIC methodology to efficiently manage Risk and Opportunity assessments, Issue Resolution procedures, and Retrospective analyses.
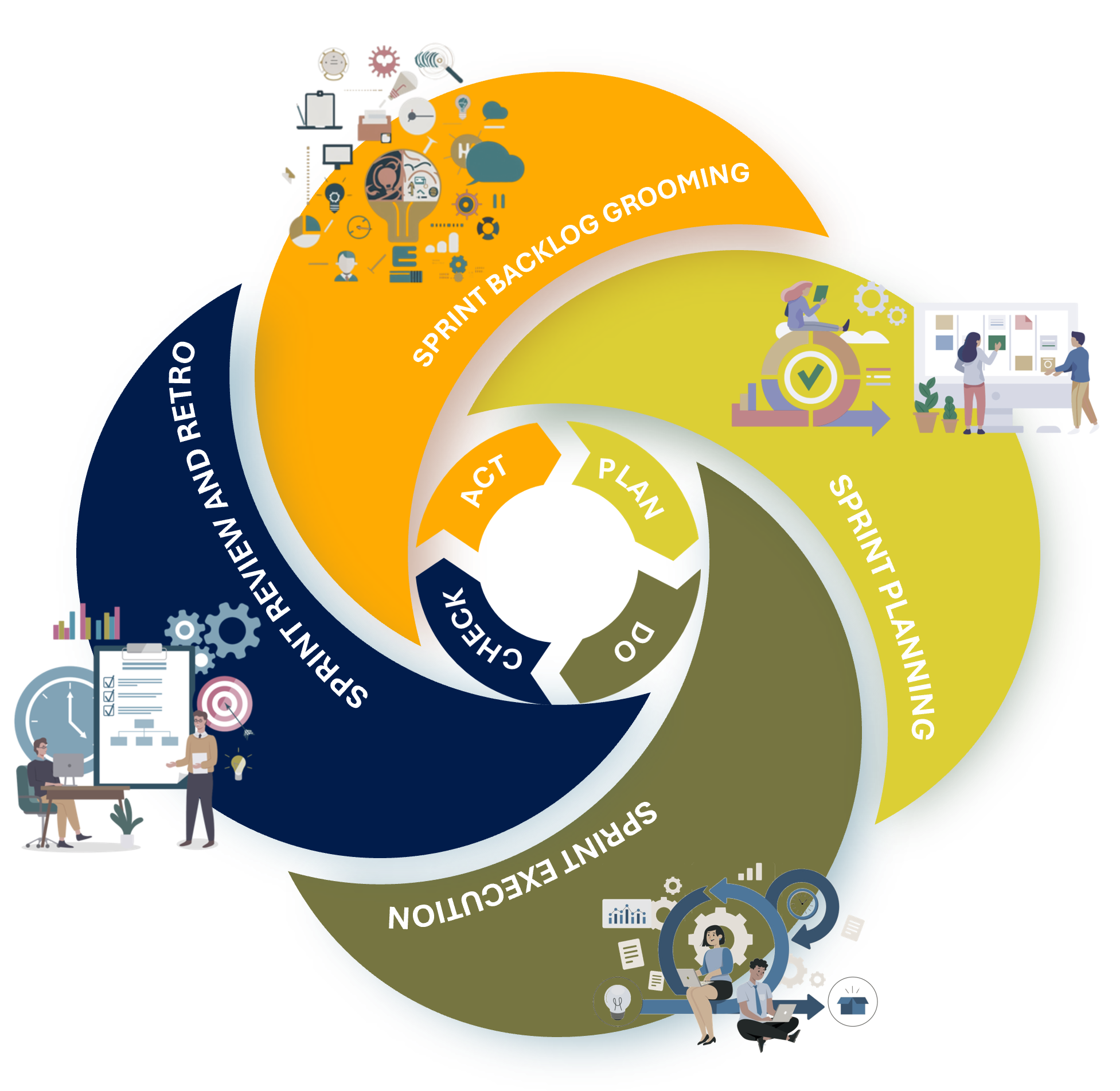
Agile Methodology and the PDCA cycle are two fundamental frameworks in project management and continuous improvement. They offer structured, iterative, and cyclical methodologies for effective delivery management and ongoing enhancement of processes. Although they stem from different disciplines, their core principles show considerable alignment, which can be utilized to establish an efficient and organized approach that promotes goal-oriented progress and continuous improvement.
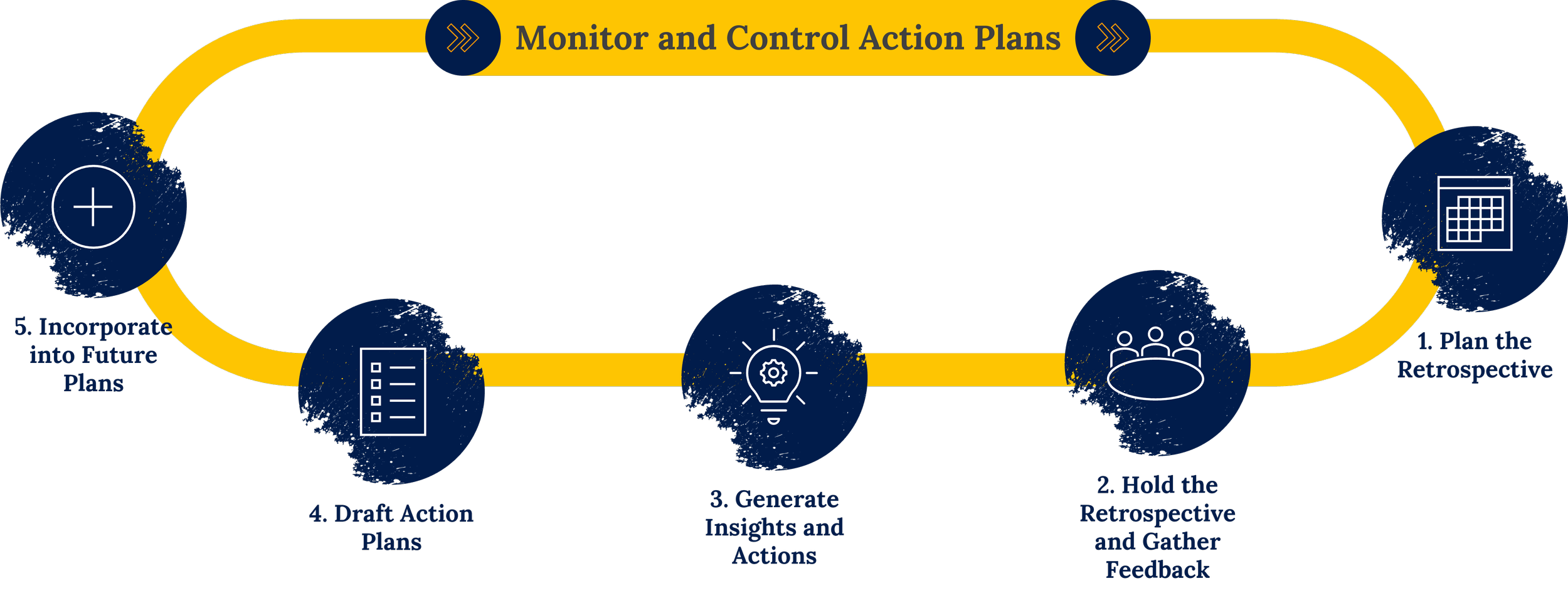
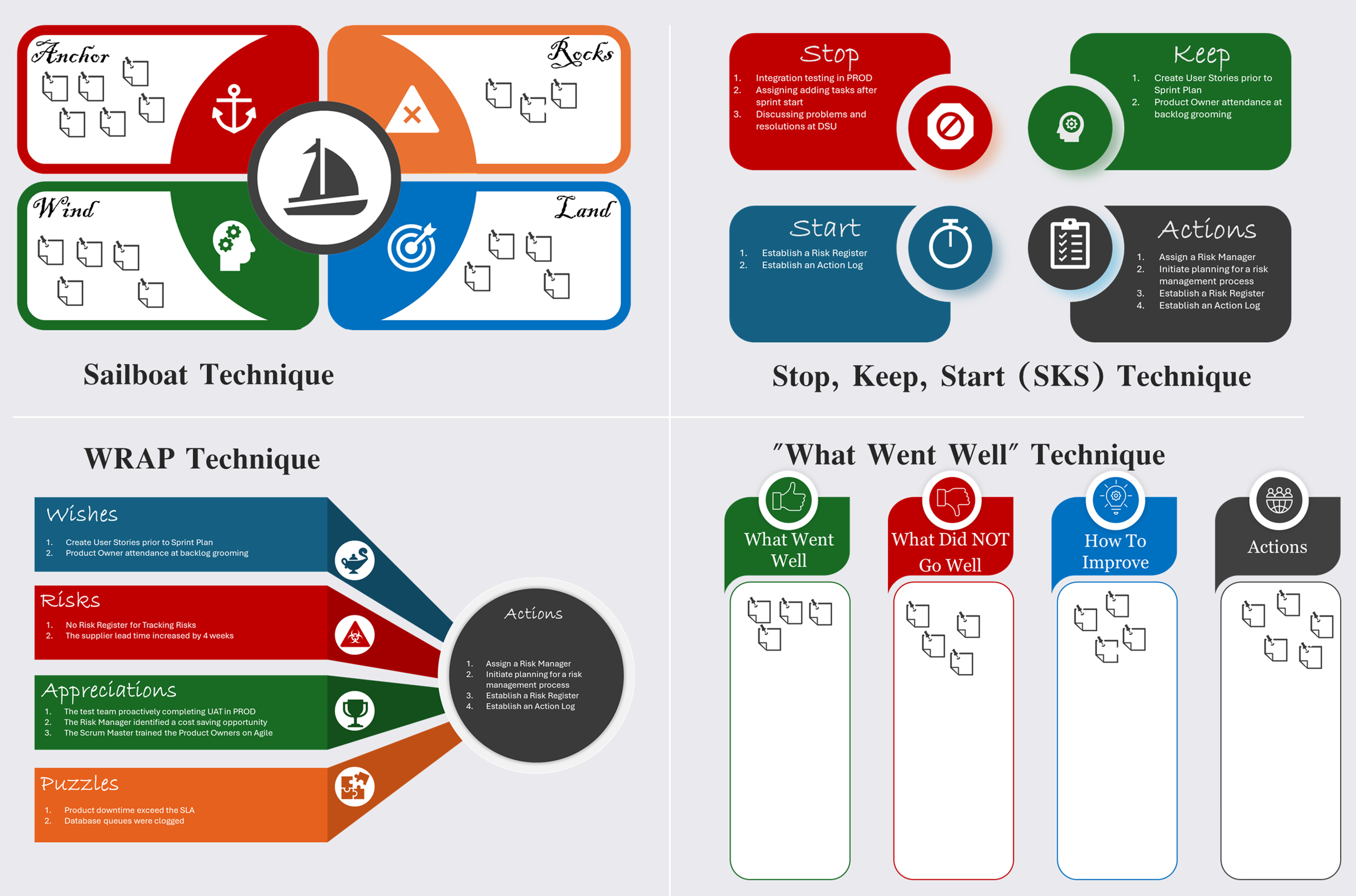
Retrospectives are an essential part of Agile methodology. Following the guidelines from PMI, Agile retrospectives are held at the end of each Sprint with the intention of improving successive Sprints. According to PMI guidance, the Scrum Master is responsible for the retrospective process. While it is common for the Scrum Master to facilitate the retrospectives, this role can be rotated among the team members.
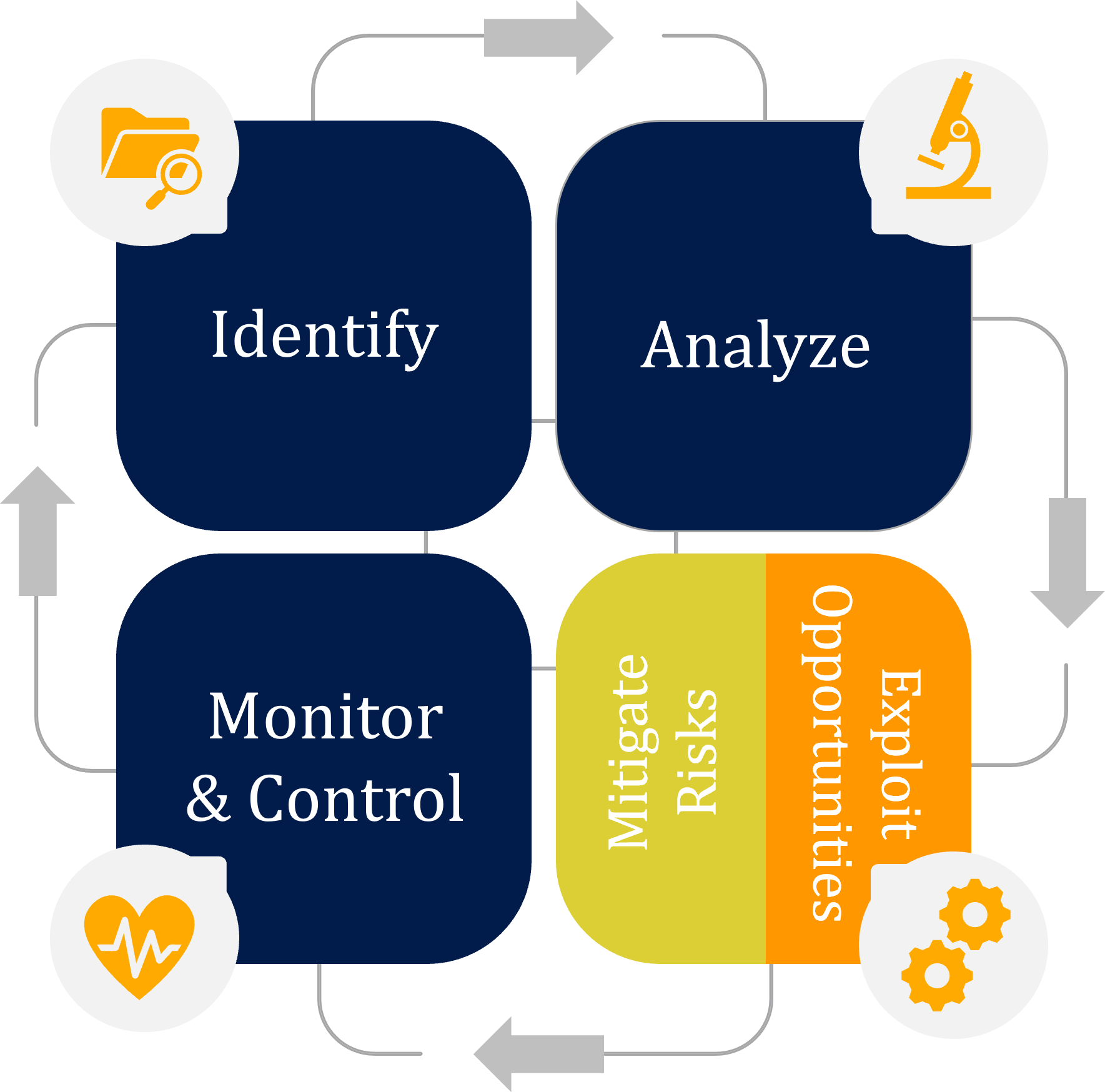
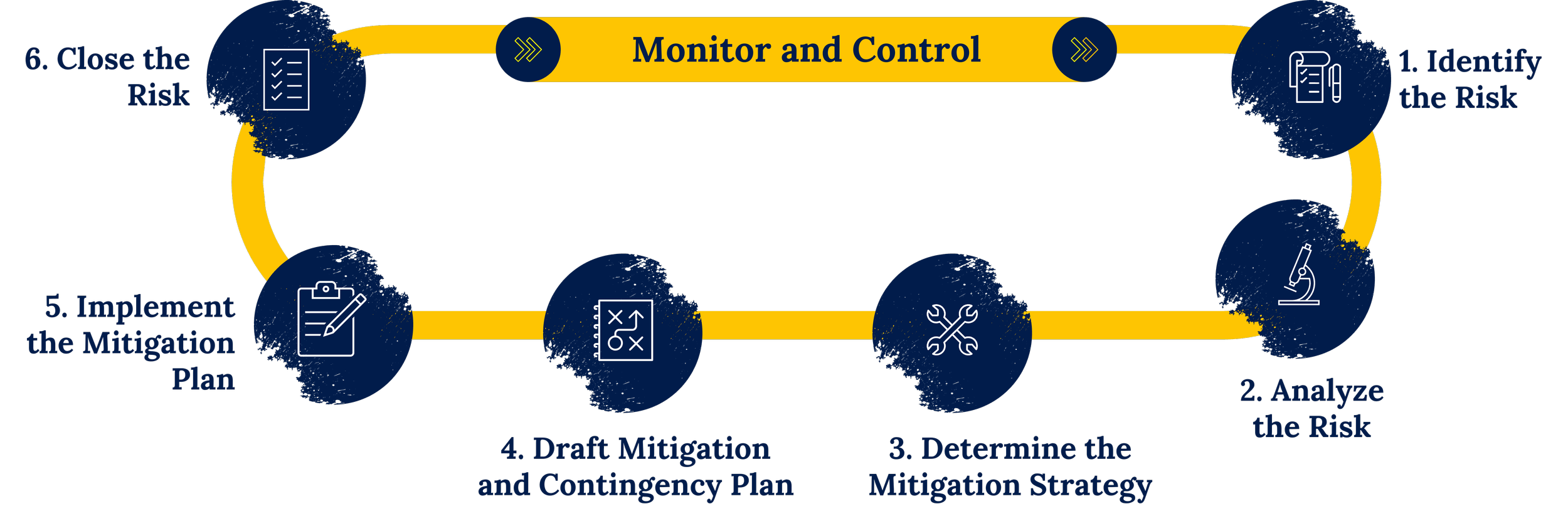
To effectively manage Risks and Opportunities, it is advisable to integrate opportunity management into risk management framework and processes. Like the risk management process, which entails identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks, the opportunity management process involves identifying opportunities, analyzing their likelihood and impact, and strategically exploiting them to maximize benefits.
Requirements documents are living documents that must evolve and be updated consistently and continuously to reflect changes as the project matures and new discoveries or clarifications are made. However, not all Requirements Documents are the same. There are at least 10+ Requirement Document types that are widely used across public and private sectors. They serve unique purposes with specific objectives.
An IMS is a comprehensive, time-phased plan that integrates all project tasks, milestones, and dependencies into a unified framework to guide project execution. Often used in large and complex projects, an IMS serves as a central planning tool to ensure alignment among all stakeholders and project teams. However, the IMS is more than just a timeline; it is a dynamic tool that reflects the project scope, schedule, and resource allocation in detail.
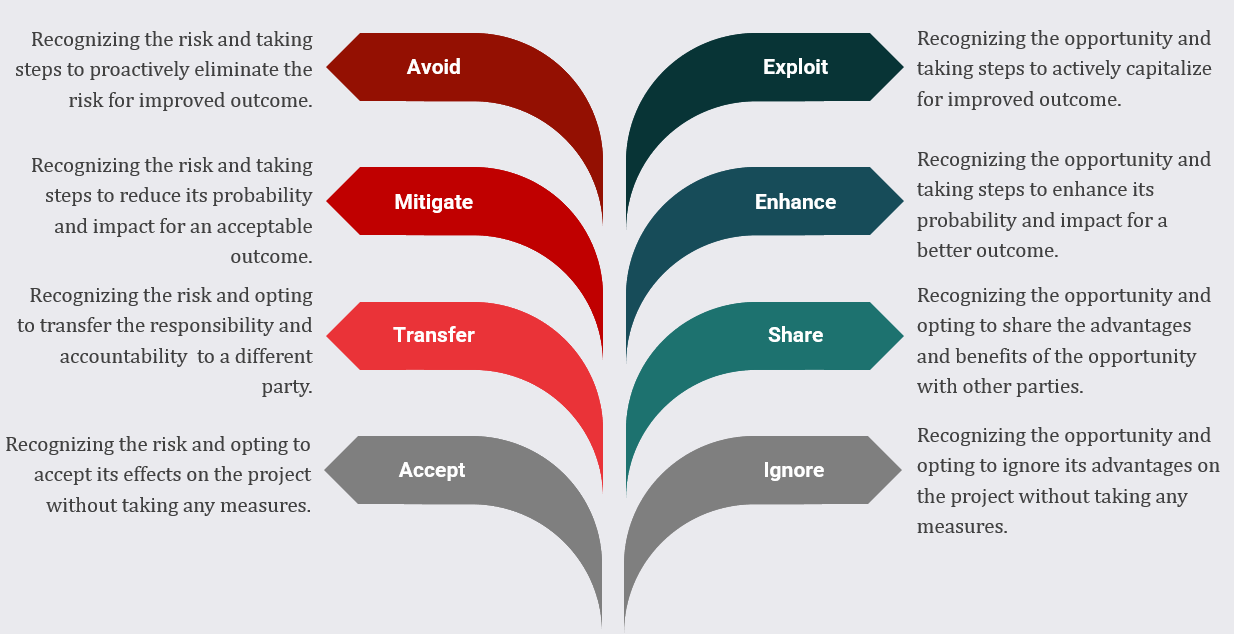
To effectively manage Risks and Opportunities, it is advisable to integrate opportunity management into risk management framework and processes. While risks response strategies include accepting, transferring, mitigating, or avoiding risks, the corresponding opportunity response strategies include exploiting, enhancing, sharing, or ignoring an opportunity.
The risk management process within an organization is a procedure aimed at anticipating and mitigating risks. The process reduces or avoids adverse outcomes and enhances the probability of achieving project objectives successfully. The primary objective of the risk management process is to proactively identify, analyze, and address potential risks that could adversely affect project schedule, cost, quality, and customer perception.
A retrospective is a structured meeting in which a project team reflects on a previous iteration or phase, assesses its performance, identifies areas for improvement, and formulates a plan for future work. The main objective of a retrospective is to promote continuous improvement by deriving lessons from past experiences.
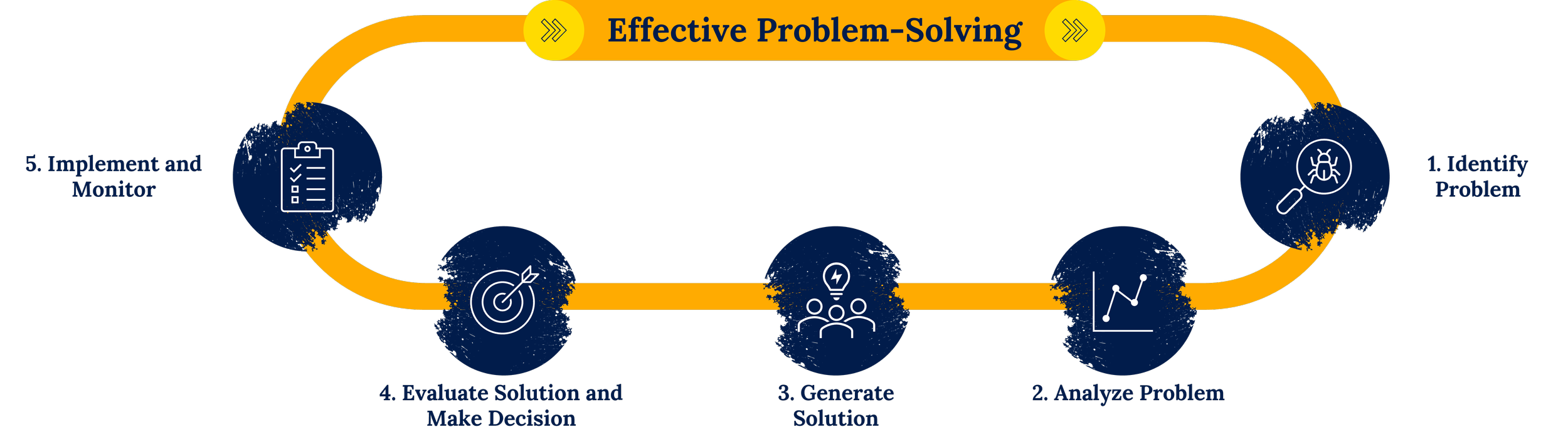
Problem-solving is at the heart of successful project management, offering a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and addressing challenges that arise throughout the project lifecycle. Its primary purpose is to ensure that obstacles do not derail progress but instead serve as opportunities to modernize and improve.
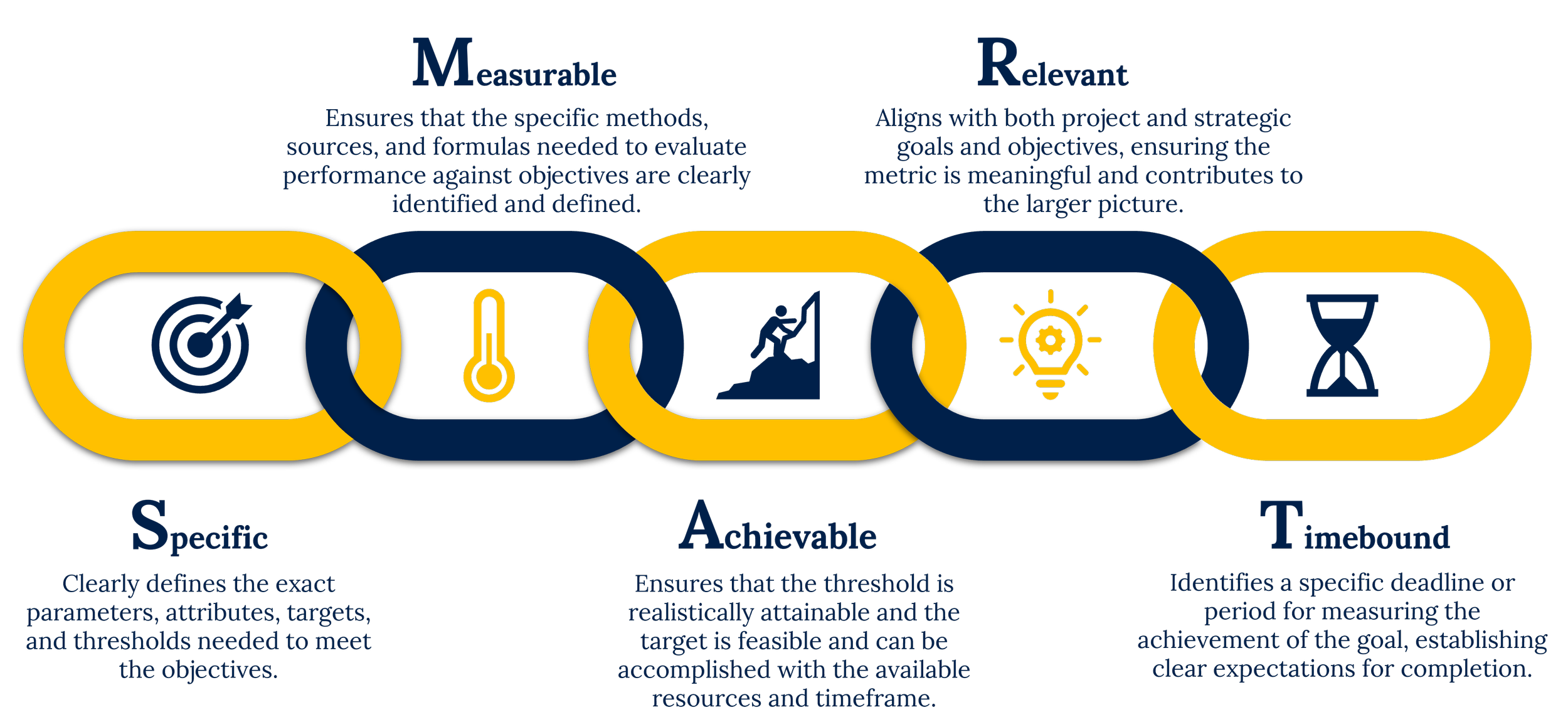
SMART goals are designed to address all key functions, processes, and deliverables. The purpose of goals is to direct attention and resources towards what is most important in order to successfully achieve project objectives and priorities. SMART metrics help ensure that objectives are both ambitious and practical, allowing teams to track progress effectively while staying aligned with broader priorities.
Agile frameworks, methodologies, tools, and techniques serve as fundamental pillars in establishing robust and adaptable structures within project management. While they are inherently interconnected, each possesses distinct definitions, boundaries, and mechanisms of control that are vital to the success of agile implementation. The image illustrates a comprehensive overview of the various frameworks, methodologies, tools, and techniques used in Agile implementation.
A Kanban board is a highly effective visual project management tool designed to help teams manage, track, and optimize workflows efficiently. By utilizing columns to represent different stages of a process and cards to signify individual tasks, the board provides a clear and organized visualization of ongoing work. This setup not only highlights the current status of tasks but also enables teams to identify delays, monitor work-in-progress (WIP), and streamline overall task progress. The dynamic nature of the Kanban board ensures adaptability and fosters a collaborative, transparent working environment, making it an indispensable asset for teams aiming to enhance productivity and workflow clarity.
Scrum is characterized by short, iterative cycles known as Sprints, each aimed at delivering a usable increment of goods and services. The methodology promotes close collaboration between cross-functional teams and stakeholders to ensure the delivery meets or exceeds requirements. The collection and analysis of regular feedback are essential components of Agile Scrum Methodology. This process allows teams to refine and adjust their work based on insights and experiences gathered during retrospectives and reviews. It underscores the importance of continuous improvement through regular evaluations and adaptations.
For project delivery, the two most widely recognized methodologies adopted across various industries are Waterfall and Agile. Project teams often believe they must choose between the traditional Waterfall methodology and the relatively newer Agile Scrum methodology. However, there is a third option where projects can incorporate elements from both methodologies effectively to achieve successful delivery and completion. Each methodology offers distinct advantages that can be leveraged for improved outcomes.
Stakeholder engagement refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and actively involving stakeholders throughout the project's lifecycle. The Influence-Interest Grid is a common presentation style using a two-dimensional matrix. Interest and influence are shown along with a third dimension, often represented by the color or size of symbols classifying stakeholders as Leaders, Advocates, or Blockers.
Stakeholder engagement refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and actively involving stakeholders throughout the project's lifecycle. SEAM is a project management tool used to analyze and document the current (C) and desired (D) state of stakeholder engagement. It classifies stakeholders according to their degree of interest, influence, and vested role, allowing project managers to evaluate and implement strategies that enhance the desired engagement.
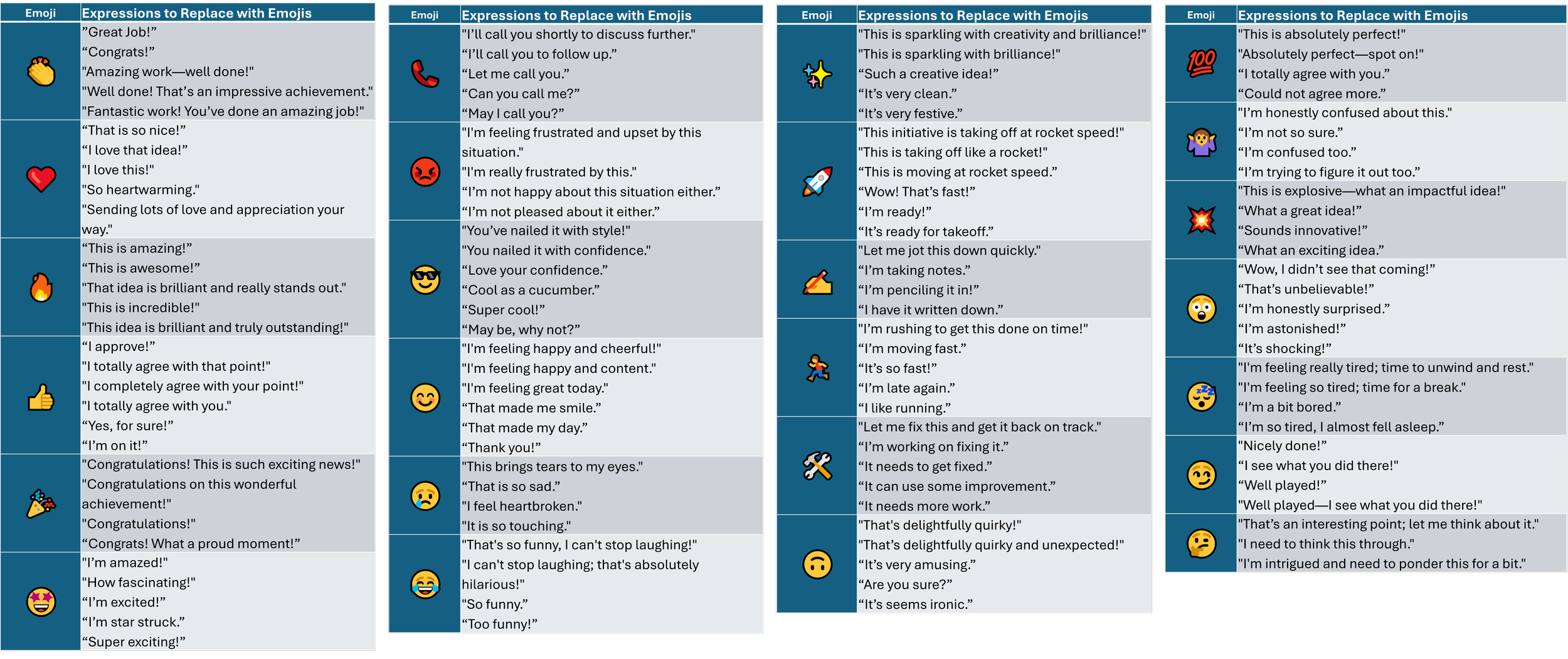
While emojis are undeniably a creative and engaging addition to digital communication, their role in professional settings, particularly in project management, is complex. On one hand, a well-placed emoji can add empathy, break the monotony of formal exchanges, or clarify the tone of a message. On the other hand, their subjective interpretation often leaves room for misunderstandings, especially in scenarios that demand precision and unambiguous dialog.
There are various techniques for gathering feedback and input during retrospectives. Project managers have the option to select from existing techniques or design and customize one that best suits the project. For successful implementation, it is imperative that the team understands how the technique works in practice. Therefore, when designing the process, it is important to focus on clarity and simplicity to achieve the best results.